When applying for bankruptcy, your ability to select the right type can mean the difference between success and failure. Although it is never recommended to file a bankruptcy petition without speaking with a qualified attorney, it is equally important to know what to expect in order to make the right choice and not proceed to the filing process blindly.
For this reason, we have created the following overview highlighting the differences between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 Bankruptcy.
Ohio Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
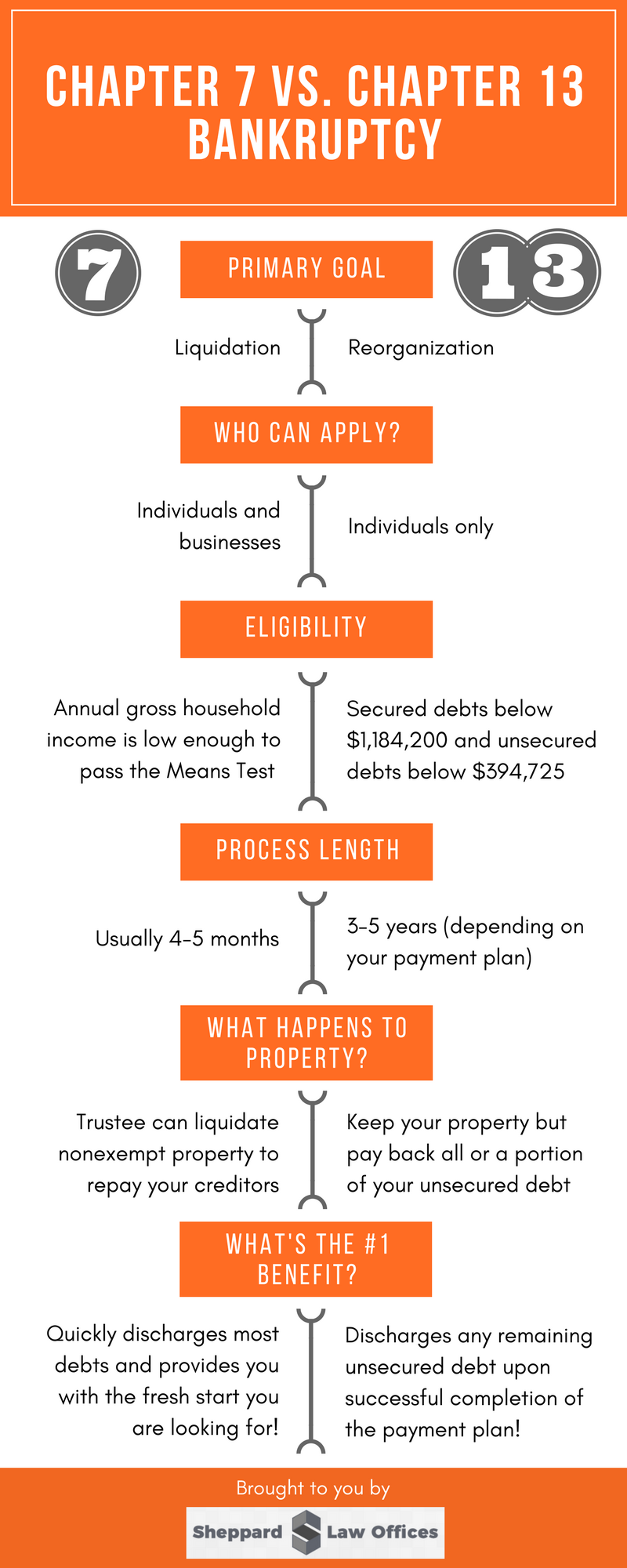
The primary goal of a Chapter 7 petition is a complete liquidation of debt. Under the Ohio Bankruptcy Code, you are able to keep your exempt property and an assigned trustee sells your non-exempt assets to repay your creditors. You are also able to keep the cash value of your insurance policies, retirement benefits, the majority of personal property, public benefits (such as welfare and unemployment benefits), and any tools used in your work.
Both individuals and businesses are eligible for liquidation of debt under Chapter 7.
Ohio Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
The primary goal of a Chapter 13 petition is a reorganization of your finances as well as a plan for a better financial future. In order to qualify, you must prove to the bankruptcy court that you have sufficient regular income to support a repayment plan – once your reasonable expenses are subtracted. An unemployed spouse can use the working spouse’s salary as a source of income. You are able to keep all of your property but must pay back all or a portion of your unsecured debt.
Businesses are not eligible for this bankruptcy petition, as there is a similar form of reorganization under Chapter 11 specifically aimed at business owners. However, a business owner can file as an individual under Chapter 13.
Which Should I Use – Chapter 7 or Chapter 13?
If you qualify for both types of bankruptcy, you are typically free to select the type that you and your bankruptcy attorney see fit. However, you cannot apply for Chapter 7 unless your income is low enough to pass the Means Test. Similarly, you cannot apply for Chapter 13 unless your secured debts are below $1,184,200 and your unsecured debts are below $394,725.
The primary benefit of Chapter 13, on the other hand, is that discharges any remaining unsecured debt upon successful completion of the payment plan. Additionally, it provides you with a second chance to catch up on any overdue payments.
To learn more about the differences between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy, please call bankruptcy attorney Kenneth L. Sheppard, Jr. from Sheppard Law Offices today! We will be happy to help select the ideal option for your unique situation.
What is the #1 Benefit of Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
The primary benefit of Chapter 7 bankruptcy is that it quickly discharges the majority of your debts, thereby providing you with the fresh start that you were looking for.
What is the #1 Benefit of Chapter 13 Bankruptcy?